
Generally, there are three characteristics of sound:
- frequency affects pitch of the sound
- amplitude affects loudness of the sound
- wave form affects quality of the sound
1. Frequency - Pitch
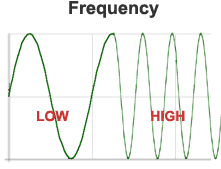
The frequency of a wave is measured as the number of complete vibrations of particles of a medium per unit time. A commonly used unit for frequency is Hertz.
Pitch is an auditory sensation in which listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based on the frequency of sound. A high pitch sound corresponds to a high frequency sound wave and low pitch sound corresponds to a low frequency sound wave.
Changing Pitch:
A string vibrates with a particular fundamental frequency. However, it is possible, to produce pitches with different frequencies from the same string. The 4 properties of the string that affect its frequency are length, diameter, tension and density. The properties are as described:
- When the length of a string is changed, it will vibrate with a different frequency. Shorter strings have higher frequency and therefore higher pitch.
- Diameter is the thickness of the string. Thick strings with large diameters vibrate slower and have lower frequencies than thin ones.
- Tightening the string gives it a higher frequency while loosening it gives it a lower frequency.
- The density of a string also affects its frequency. The denser the string, its molecules vibrate slower and its frequency will be lower.
Name
|
Frequency Range (Hz)
|
Characteristics
|
0 - 20
|
Very low frequencies of sound that the human ear can’t detect, but you mayfeel the rumbling of the waves through your body.
| |
Sonic (AKA Audio)
|
20 - 20 000
|
Normal range for human ears, although not everyone (especially the elderly) will hear to the extremes of this range.
|
20 000 +
|
Beyond normal hearing for humans, although some animals (like dogs) hear part ways into this range. Also used in medicine (e.g. ultrasounds for pregnant women).
|









.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment